Security foundations
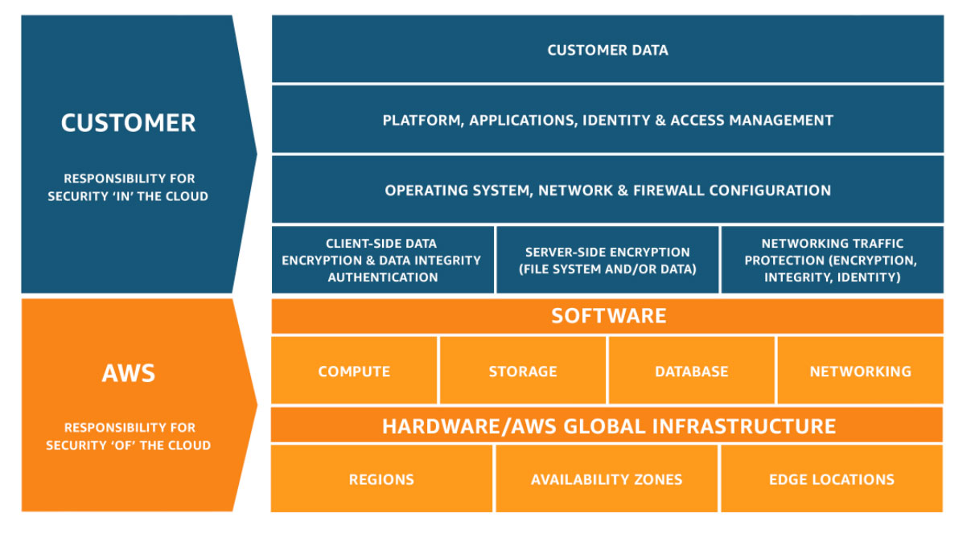
Share responsibility
-
AWS Responsibilities “Cloud Security” – AWS is responsible for protecting the infrastructure that runs all services provided in the AWS Cloud. This infrastructure includes the hardware, software, networks, and facilities that run AWS Cloud services.
-
Customer Responsibilities “Cloud Security” – Customer responsibilities will be determined by the AWS Cloud services the customer selects. This determines the amount of configuration work that customers must perform as part of their security responsibilities
Administration
- Security governance, as a subset of the overall approach, aims to support business objectives by defining policies and control objectives to help manage risk. Achieve risk management by following a layered approach to security control objectives – each layer builds on the previous layer.
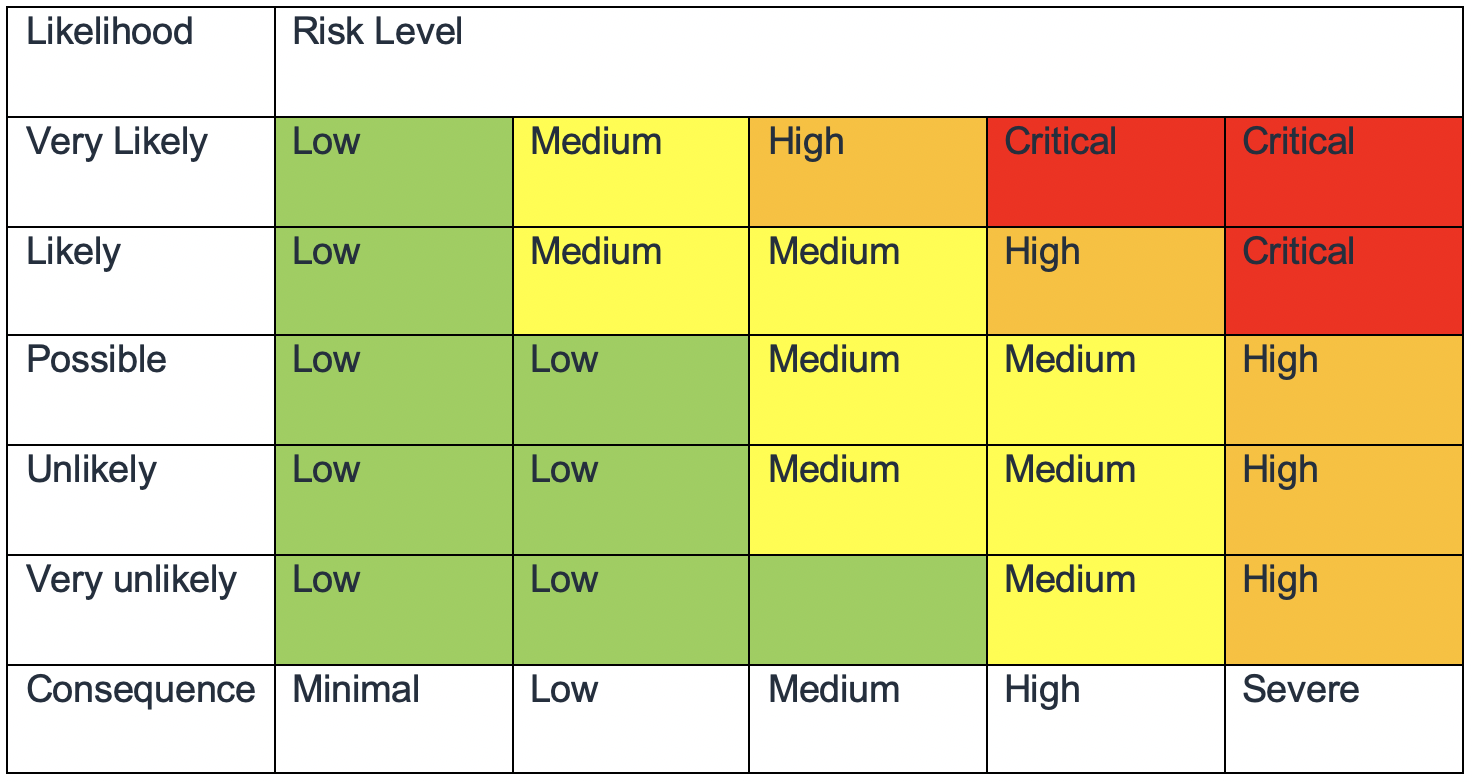
- No matter where you implement controls, the goal is the same: manage risk. A variety of risk management frameworks apply to specific industries, regions or technologies. Your main goal: highlight risks based on likelihood and consequences
AWS account management and segmentation
AWS recommends that you organize workloads in separate accounts and group accounts based on functionality, compliance requirements, or a common set of controls rather than reflecting your organization’s reporting structure. In AWS, an account is a rigid boundary. For example, you should isolate the account level to separate production workloads from development and test workloads.
- Centralized account management: AWS Organizations automates the creation and management of AWS accounts and controls them once they are created.
- Set centralized controls: Control what your AWS account can do by only allowing specific services, Regions, and service actions at the appropriate level. AWS Organizations enables you to use service control policies (SCPs) to apply permission protections at the organization, organizational unit, or account level, applicable to all users and roles* AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM).*
- Configure services and resources centrally: AWS Organizations helps you configure AWS services that apply to all your accounts. For example, you can configure centralized logging for all actions performed in your organization using AWS CloudTrail and prevent member accounts from deactivating logging sign. You can also centrally aggregate data for the rules you define using AWS Config, allowing you to check your workloads for compliance and react quickly to changes. change. AWS CloudFormation StackSets allows you to centrally manage AWS CloudFormation stacks across accounts and OUs within your organization. This allows you to automatically provision new accounts to meet your security requirements.
- AWS services, such as GuardDuty, Security Hub, and AWS Config, support integration with AWS Organizations, including assigning a specific account for administrative functions.